International Transport to Kazakhstan via Iran: A Comprehensive Overview
Introduction
Kazakhstan, Central Asia’s largest country, is strategically positioned at the crossroads of Europe and Asia. Its vast territory, rich resources, and growing economy present significant opportunities for trade and business. As global trade routes are continuously evolving, Iran has emerged as a crucial transit country for international transportation to Kazakhstan. This article delves into the intricacies of international transport to Kazakhstan via Iran, including logistics, trade considerations, regulatory aspects, and the advantages of this route.
Overview of Kazakhstan’s Trade Landscape
Kazakhstan is rich in natural resources, including vast reserves of oil, natural gas, minerals, and agricultural products. As a member of the Eurasian Economic Union (EAEU) and the Silk Road Economic Belt initiative, Kazakhstan plays a vital role in regional trade. The country relies heavily on international transport networks for exporting its products and importing goods and services vital for its economic growth.
Key Trade Partners
Kazakhstan’s major trade partners include:
- China: The most significant partner, engaging in trade primarily in energy and raw materials.
- Russia: Another vital partner, contributing to the majority of Kazakhstan’s imports, especially in machinery and equipment.
- European Union: A growing trade partner, particularly in high-tech goods and industrial products.
- Iran: Emerging as a key transit hub for trade between Kazakhstan and other markets, especially in Asia.
Importance of Iran as a Transit Country
Iran’s geographical proximity and its logistical capabilities make it an important route for transporting goods to Kazakhstan. The extensive network of roads, railways, and maritime routes in Iran facilitates smoother transit operations, offering several advantages:
- Shortened Transit Times: The route via Iran significantly reduces transit times between Asia and Kazakhstan compared to other routes.
- Diverse Transport Modes: Iran offers various transport modes, including road, rail, and sea, thereby providing flexibility in logistics planning.
- Strategic Trade Agreements: Iran has signed several treaties and agreements promoting trade with neighboring countries, including Kazakhstan, enhancing cooperation in transport and logistics.
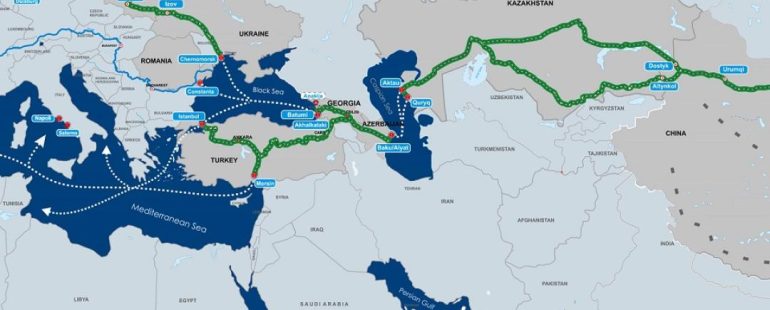
Transportation Routes from Iran to Kazakhstan
1. Road Transport
Road transport is a primary mode of international transport between Iran and Kazakhstan. The most common routes include:
- Tehran to Almaty: The road journey from Iran’s capital to Kazakhstan’s largest city usually involves crossing the Caspian Sea by ferry to Aktau and then continuing by road or rail to Almaty.
- Mashhad to Aktobe: This route offers an efficient overland connection, facilitating trade in agricultural products and manufactured goods.
2. Rail Transport
The Iran-Kazakhstan railway route is a critical link for freight transport. Key features include:
- Trans-Caspian International Transport Route (TITR): This corridor links China, Kazakhstan, and Europe, passing through Iran. The route utilizes a combination of rail networks and ferry services across the Caspian Sea, providing an alternative to traditional routes.
- Kazakhstan-Iran Railway Project: Ongoing developments in railway infrastructure, such as the Kazakhstan-Turkmenistan-Iran railway, are enhancing connectivity.
3. Maritime Transport
While less dominant than road and rail, maritime transport is essential for certain types of cargo, especially bulk goods and oil products:
- Caspian Sea Shipping: Ferries and cargo vessels connect the Iranian ports (such as Anzali and Amirabad) to Aktau in Kazakhstan, allowing for substantial cargo shipments.
Regulatory Framework
Navigating the regulatory landscape for transporting goods through Iran to Kazakhstan involves several considerations:
- Customs Regulations: Both Iran and Kazakhstan have customs protocols that must be adhered to for smooth transit. This includes tariff classifications, customs duties, and declarations.
- Bilateral Agreements: Iran and Kazakhstan have entered into various agreements to foster trade, including the Free Trade Agreement (FTA) under the EAEU framework, which facilitates easier customs procedures and reduced tariffs.
- Transport Licensing: Carriers must obtain necessary permits and licenses to operate across borders, which may involve coordination with both Iranian and Kazakh authorities.
Challenges and Considerations
While the transport route via Iran offers many advantages, several challenges must be addressed:
- Geopolitical Issues: Political tensions in the region may impact trade flows and customs processes.
- Infrastructure Development: Continued investment in infrastructure is necessary to keep up with growing trade volumes and improve logistics efficiency.
- Language Barriers: Communication can sometimes pose issues, as customs and transport officials may speak different languages.
Future Prospects
The future of international transport to Kazakhstan via Iran looks promising. With the rapid development of infrastructure in both countries and ongoing regional cooperation, trade is likely to expand significantly. Key drivers include:
- Investment in Transport Infrastructure: Both Kazakhstan and Iran are investing in enhanced transport networks, which will improve road and rail connectivity.
- Increased Demand for Trade: As Kazakhstan continues to grow its economy, demand for imported goods will rise, boosting transit volumes through Iran.
- New Trade Agreements: Future agreements and greater collaboration on customs processes are likely to ease trade and logistics.
Conclusion
International transport to Kazakhstan via Iran presents a viable and increasingly attractive route for businesses looking to engage in trade within Central Asia and beyond. While challenges exist, the strategic advantages and evolving infrastructure in Iran and Kazakhstan position this route as a key player in the region’s logistics landscape. By understanding the complexities and harnessing the opportunities, businesses can effectively tap into the growing markets in Kazakhstan and utilize Iran as a crucial transit hub.

Comments (No Responses )
No comments yet.