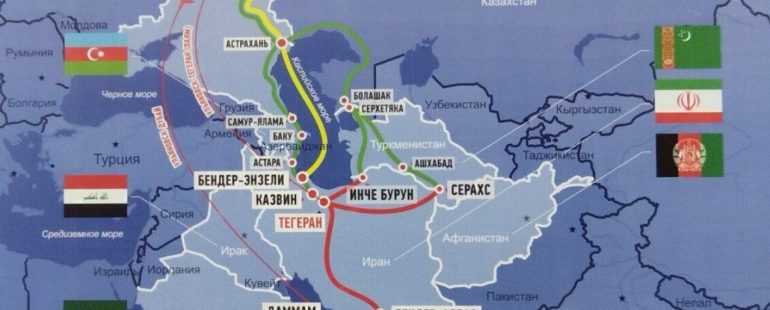
International Export to Russia via Iran
The economic landscape of international trade has been evolving significantly in recent years, particularly in the context of geopolitical shifts and sanctions. One notable corridor that has emerged is the route of exporting goods to Russia through Iran. This article explores the dynamics of this trade route, the strategic importance of Iran as a transit country, the sectors involved, challenges faced, and future prospects.
Strategic Importance of Iran
Geographical Position
Iran’s geographical position makes it a critical transit hub connecting the Middle East, Central Asia, and Europe. It shares borders with several countries, including Turkey, Iraq, and Afghanistan, and has access to the Caspian Sea. This connectivity allows it to facilitate trade between its neighbors and broader international markets, including Russia.
Political Relationships
Iran and Russia have developed a multifaceted relationship, characterized by cooperation in political, military, and economic spheres. Both nations have often found common ground in opposing Western influence and sanctions, thus fostering a partnership that extends to economic collaboration, particularly in times of heightened sanctions against Iran and Russia from Western nations.
Trade Dynamics
Key Sectors
- Energy: One of the strongest ties between Iran and Russia is in the energy sector. Both countries are major oil and gas producers. Iran exports crude oil and refined petroleum products to Russia, which in turn, facilitates the export of oil-related technologies and services to Iran, enhancing collaboration in energy projects.
- Agriculture: Iran has positioned itself as a key supplier of agricultural products to Russia. Persian pistachios, saffron, and various fruits are examples of goods that have found a solid market in Russia due to the growing demand for diverse and exotic foods.
- Consumer Goods: With the imposition of Western sanctions, Russia has started to look towards Iran for consumer goods, including textiles, electronics, medical supplies, and household products, which are increasingly entering the Russian market via Iranian trade networks.
Trade Routes
The trade routes from Iran to Russia can be divided into several modalities:
- Land Transportation: Trucks and rail networks are extensively used for transporting goods across the borders. Key routes include the Qazvin-Rasht-Astara corridor, which connects Iran to the Caspian Sea, and further on to Russia.
- Maritime Transport: Goods can be transported from Iranian ports, such as Bandar Abbas, to Russian ports on the Caspian Sea, including Astrakhan. This route is gaining popularity for bulkier cargo.
- Air Transport: Although more costly, air freight options have also been occuring for high-value goods, which need to be imported quickly.
Trade Agreements and Facilitation
The establishment of the Iran-Russia Joint Trade Council seeks to streamline the trade process and reduce barriers. Bilateral trade agreements aim to enhance economic collaborations and facilitate smoother customs procedures.
Challenges Faced
Sanctions
Both Iran and Russia are subject to various international sanctions, which complicate trade efforts. The sanctions create significant legal and financial risks for businesses involved in trade with these nations.
Infrastructure
While Iran boasts extensive transportation networks, infrastructural improvements are still necessary to accommodate increased trade volume. Upgrades to ports, roads, and rail systems will be essential for maintaining efficiency.
Bureaucratic Hurdles
The complexities of navigating through customs regulations can create delays and additional costs. Companies need to ensure compliance with both Iranian and Russian import/export regulations.
Security Concerns
Geopolitical tensions in the region, especially involving neighboring countries, create a somewhat unpredictable security scenario that companies must navigate when planning logistics.
Future Prospects
Growing Demand
As Russia continues to diversify its trade partnerships, the demand for Iranian goods is likely to increase. The agricultural and energy sectors are seen as particularly promising, given the existing collaborations.
Expansion of Trade Agreements
The potential for enhanced trade agreements targeting specific sectors could facilitate smoother and more efficient trade. Both countries may look to capitalize on each other’s strengths to foster economic growth through mutual cooperation.
Development of New Trade Routes
With ongoing investment in transportation infrastructure aimed at improving international logistics, both land and maritime routes between Iran and Russia could see significant development, potentially increasing trade volume.
Conclusion
International export to Russia via Iran is more than a simple logistical operation; it is a reflection of changing global dynamics in trade, economy, and geopolitics. As both nations navigate the complexities of sanctions and global economic changes, their partnership seems poised to strengthen further. By addressing existing challenges and maximizing opportunities, Iran could emerge as an increasingly vital hub for exports to Russia, fostering economic interdependence in an evolving landscape.

Comments (No Responses )
No comments yet.